Despite the trend in modern software development to the web and mobile platforms, desktop applications are still all around us. When it comes to Line-of-Business-Apps, many applications solely run on Windows desktop machines.
Most developers have to deal with existing applications. When we read the news about upcoming changes to .NET Core or the shiny new things like Blazor or Web assembly we kind of feel left out.
What we need to keep in mind is that there is also innovation happening in the .NET development for Windows desktop applications. When it comes to migrating old projects to newer frameworks or when we have to choose a stack for an entirely new application we have many choices.
This article intends to give an overview of all the choices available and to give (sometimes opinionated advice) on when to choose which technology stack for your (next) application.
In this article, we’re going to take a look at the following technologies:
Win32 and COM
The oldest still viable approach to build a Windows desktop application is using C++ and the Win32 APIs. Granted, it’s not the newest and hottest technology stack, but it’s still in use, and the applications run on most Windows versions.
Win32 has been introduced in late 1995 with the release of Windows 95 and is available in all following Windows releases including Windows 10.
Modernizing an application written using C++ and the Win32 APIs is a hard task. I do not know about anything else than rewriting the entire application using another technology stack. Most newer technologies require either Visual Basic .NET or more often C# as the programming language.
If you have another migration path than a complete rewrite – please write it in the comments below this article.
Windows Forms (WinForms)
WinForms is the Windows desktop technology stack introduced with the .NET Framework in 2002 to make desktop development much simpler. After about 15 years of closed source development, Microsoft announced to open-source WinForms on December 4th, 2018.
WinForms allows the developer to get results quickly. Visual Studio has a built-in editor which enables us to drag and drop controls from the toolbar onto the dialogs. By double-clicking onto the controls on the dialog, Visual Studio generated click handlers in the code which allow us to write the application logic.
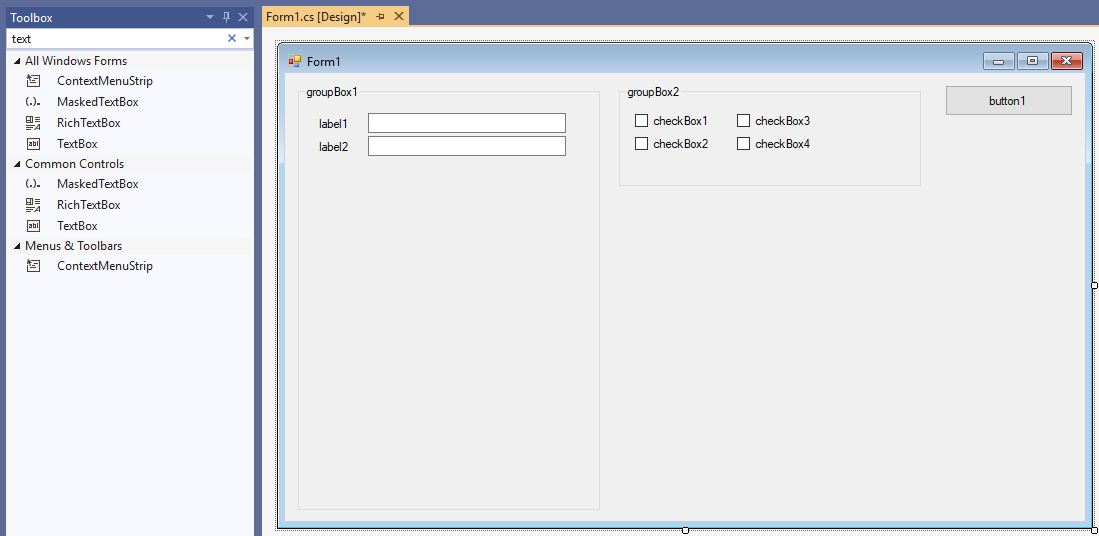
The advantages of WinForms are obvious: Rapid prototyping, gaining fast results and the opportunity to work with a graphical editor in Visual Studio to create the user interfaces. WinForms apps run on all Windows computers with an installed .NET Framework.
Because Microsoft started to bundle the .NET Framework to the Windows operating system nearly every computer runs at least one, most of the time multiple version of the .NET Framework.
The downsides of WinForms are the limited design options, the close relationship with Visual Studio which makes application development outside Visual Studio nearly impossible, and generated code which can be a pain using version control systems when multiple developers collaborate on the same project.
In my opinion, WinForms is still viable if the developer wants or needs to get a quick result, has limited experience in UI programming or programming in general and if the user experience requirements are not that big.
Microsoft announced that starting with the release of .NET Core 3.0 there will be an option to run WinForms applications on .NET Core instead of the (full) .NET Framework.
In my opinion, every application that is still being developed and runs on WinForms should be migrated to .NET Core or at least have a strategy in mind how to approach it. .NET Core has so many advantages that in most cases you don’t want to miss out on them.
Windows Presentation Framework (WPF)
With the release of .NET Framework 3.0 in 2006, Microsoft introduced the Windows Presentation Framework (WPF) as an alternative to WinForms for Windows desktop development.
The main difference between WinForms and WPF is the design language. For WinForms apps, we use the graphical designer, and for WPF applications we use XAML as a markup language to describe our user interfaces.
The advantages are obvious. Using an XML-like languages developer have full control over the structure of their user interfaces. Custom designs were enabled by WPF and implementing custom controls to build richer user experiences became possible.
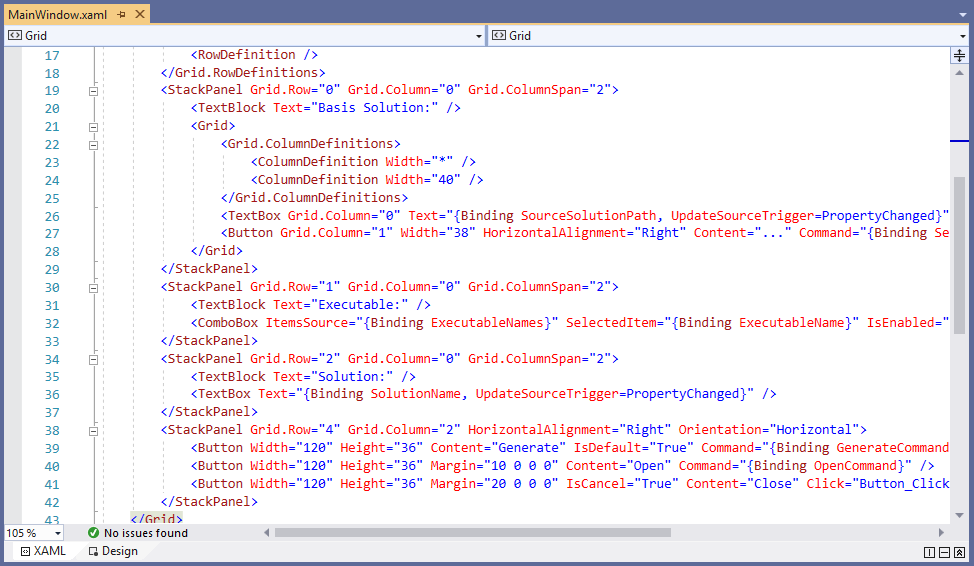
Using the data-binding mechanism and utilizing the MVVM design pattern WPF applications allow developers to split their code between user interface design code and business logic. Application logic can and should be written in class libraries with no dependency on any user interface framework. It allows for more maintainable and reusable code.
On the other side, development becomes much more demanding and requires more knowledge. Gaining results can be hard in the beginning, and there are always multiple ways to solve a problem. WinForms is often limited but forces you to a more straightforward solution on the other side.
WPF gives enormous power to the developer which allows for the option to create amazing user interfaces. If the developer puts too many elements on his dialogs or if he loads too much data at once the applications quickly feel slow. Also, WPF applications typically take longer to start compared to WinForms applications.
For a long time, WPF was the quasi-standard when it came to Windows desktop development. I worked on WPF projects from 2008 to 2018, and there are many successful projects still running on WPF.
If you need to create an application that only runs on Windows desktop computer, WPF is still a viable choice in 2019.
Microsoft announced that starting with the release of .NET Core 3.0 not only WinForms, but also WPF applications can run on .NET Core which means WPF applications can take advantage of the performance improvements of .NET Core. It’s a great thing when keeping in mind that performance is one of the most significant downsides of using WPF.
Universal Windows Platform (UWP)
UWP applications are a modern alternative to WPF and WinForms applications. UWP replaces the Windows Runtime (WinRT) and requires Windows 10.
UWP apps can be distributed using the Microsoft Store and are an excellent choice for end-user applications because the distribution of the application can be done using the Microsoft Store. It feels a lot like mobile development but for desktop computers.
UWP also runs not only on desktop computers, but also on the Xbox One, and other Microsoft devices.
UWP apps can be developed either in C# using XAML which feels a lot like writing a WPF application (with a few restrictions) or using JavaScript and HTML.
I wrote a big Introduction to the Universal Windows Platform article a few weeks ago on this blog. If you want to dive deeper into UWP apps you might want to check it out.
You’ll also find my recommendation on when to create a UWP app instead of a WPF application in the article above.
Electron (.NET)
Electron allows developing desktop applications with web technologies (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript). Electron runs your application on Chromium as a node application which means that Electron opens a browser window and lets you run your web application similar to a native desktop application.
The advantage is that Electron applications are cross-platform and also run on iOS and Linux. Some of the better-known applications using Electron include Slack, GitHub Desktop and Visual Studio Code.
On the downside, we have heavy CPU and RAM usage because the behind the scene running Chromium process consumes a lot of resources. Electron applications run on Windows 7 and newer.
Well, how is this technology related to this article? The answer is Electron.NET.
Electron.NET allows us to develop Electron applications using ASP.NET Core. We can write C# and have the same APIs as Electron offers to JavaScript developers. In general, Electron.NET comes with the same advantages and disadvantages compared to Electron.
Electron.NET can be a viable migration path for web applications that need access to computer resources that are not available on the web. It’s also an excellent technology for experienced web developers who want to get started with (Windows) desktop development in .NET.
Avalonia
Avalonia is a cross-platform XAML Framework for .NET Framework, .NET Core and Mono. Avalonia has a similar look like WPF or UWP interface definitions because it utilizes a XAML dialect for the view definitions. It also supports MVVM, data-binding and much more.
Avalonia is new which means that they do not have a lot of legacy code in their framework. Unlike WPF where there is code older than a decade that cannot be removed because of compatibility issues.
I haven’t use Avalonia in my projects, and therefore I cannot go into much detail about if I would suggest to use it for production (yet). Keep in mind that Avalonia states on their website that their framework is currently in beta phase.
What I can say though is that it’s an alternative for developers who want to go for a newer, more cutting-edge option instead of using the established WPF or UWP technologies and are not keen on putting their app in the Microsoft store.
Summary
That’s it. We covered many older and newer technology stacks which enable developers to write desktop applications using .NET programming languages. All of them come with their unique set of advantages and disadvantages.
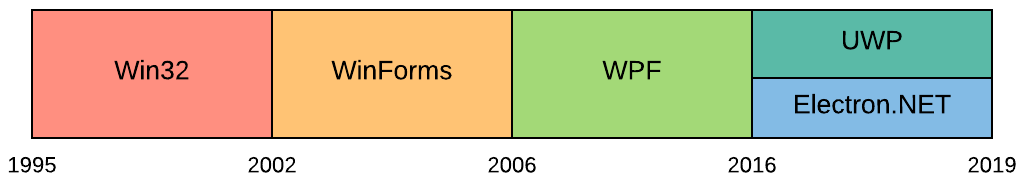
When it comes to starting a new project, WPF and UWP are choices I would recommend if you’re not sure where to start. WPF is very mature, and there is a lot of knowledge available on the Internet. UWP is a great choice if you want to make use of the Microsoft Store.
For the classic forms over data application, WinForms can be a viable choice too. Just make sure if WinForms can fulfill all the customer requirements before choosing WinForms over WPF or UWP.
For experienced ASP.NET (Core) developers stepping into the desktop world, Electron.NET can be an exciting option. It’s especially true if the application should be cross-platform.
Avalonia can be a viable choice for experimental projects or developers who want to build their product using cutting-edge technology on .NET Core.
Let me know in the comments below which technology stack you like the most and which and why you use certain technology in your current project.


